How does Ethereum co-staking work?

The second-largest cryptocurrency of the Ethereum market in 2022 is preparing for a complete transition to the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm. This event will open up new opportunities for investors to make money on the growth of the Ethereum ecosystem by becoming a validator. However, there is one caveat – at the current altcoin price, staking will be pretty expensive for users. Therefore, many platforms are already starting to offer ETH co-staking services.
What is staking?
Staking is the blocking of a certain number of coins in a smart contract to obtain the role of a validator in the cryptocurrency network. Staking is the primary way to keep the network operational in projects based on the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm. It is an alternative to mining, in which you do not need to use expensive equipment like ASIC miners or video cards with colossal power consumption.
Ethereum is still working on the Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm; it is produced precisely through mining. However, in the next couple of years, it is planned to entirely switch to the second version of the cryptocurrency protocol with PoS support, where the validators will be involved in ensuring network security.
How to become a staking validator?
To get the role of a validator, you need to open a smart contract for the ETH deposit. In this case, the minimum deposit is 32 ETH if the crypto investor wants to become a validator. At the current market price of Ethereum, that’s roughly $ 150,000.
The thing is that in its current form, cryptocurrency provides a relatively low bandwidth. ETH transaction fees are measured in tens of dollars, making work with decentralized applications on the project platform too costly. PoS, by its architecture, can provide throughput at the level of tens of thousands of transactions. In addition, the upgrade will increase the overall decentralization of the network.
Staking problems
There are several disadvantages to ETH staking. The first is that the entry threshold is too high. Not every crypto investor has $ 150,000 to become a validator. From this, it follows that only the wealthiest network participants can get the role, which means that this is also, to some extent, centralization.
The second drawback is the need to maintain a working node of the network 24/7. This node belongs to the validator and confirms transactions in blocks. Such equipment must have a consistently fast Internet connection and constant maintenance since certain sanctions can be obtained for shutting down a node.
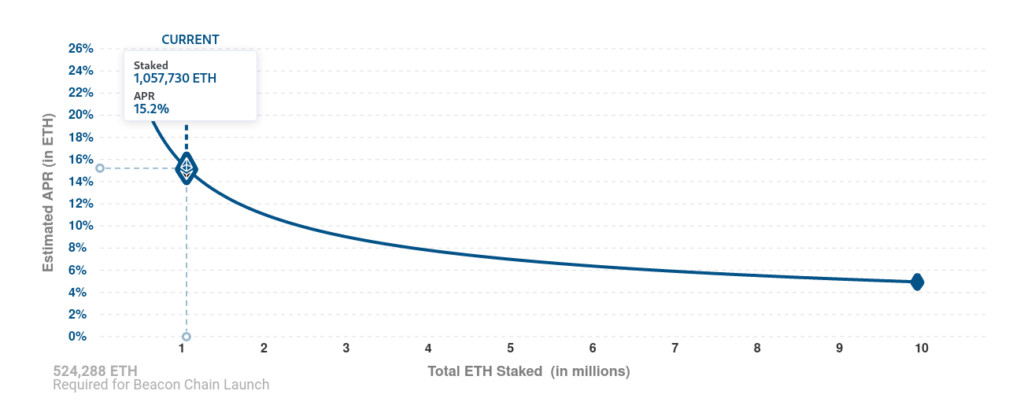
By the way, the number of sanctions includes the ability to withdraw coins blocked in a smart contract by an unscrupulous validator. They also guarantee to receive passive income for their activities up to 18 percent per annum. However, the profitability itself is not constant and will depend on the total number of validators in the network. More accurate profit information will become available closer to the final PoS transition.
Ethereum co-staking
What if you don’t have 32 ETH but want to become a validator? In this case, you can participate in the joint staking of Ethereum. The principle here is quite simple – the user deposits their funds in a shared pool or platform, which invests ETH in a smart contract and pays profits to investors. There are three joint staking options, which we will discuss below.
Staking pools
A pool is an intermediate link between those with less than 32 ETH and a smart contract. The Ethereum staking pool pools funds and pays out validator rewards in proportion to contributions. The storage of funds is carried out on a decentralized basis and can be verified in any blockchain browser.
Pools can issue their payout tokens, equivalent to invested ETH and passive income. Pool income is taken from user fees. Hashmart will introduce an investment opportunity to our staking pool this December. Thanks to Hashmart, you can also become a member of the Ethereum 2.0 ecosystem and get a reliable source of passive income.
Lending platforms
So far, only one lending platform called LiquidStake allows staking use blocked ETHs as collateral for obtaining a loan. This service also combines investor funds and transfers them to a smart contract to profit. However, there is one significant difference – the invested ETH can still be used as collateral in various Defi applications to obtain a loan. Thus, capital can be made more liquid and used in other investment instruments thanks to the lending platform.
Exchanges and custodians
One of the most accessible options is to transfer ETH to a wallet on an exchange or another custodian service offering rewards for joint staking Ethereum. However, there is a classic risk of working with a centralized exchange: the user does not control the private keys of his account.
At the moment, staking Ethereum through an exchange can undoubtedly be the easiest method. An investor needs to register or use an existing account on the exchange, deposit, or buy ETH and initiate staking through an intuitive interface. Today this is possible on many exchanges, but since it is risky to bet on innovation through a little-known exchange, we recommend using only the most reputable ones. For example, Binance, Huobi, Coinbase, Kraken, and OKEx can be relatively safe staking platforms.
Conclusion
Joint staking is an excellent tool to keep the network decentralized and grow relatively small capital. The only risk is choosing the right intermediary for depositing funds. Fortunately, our readers no longer need to look for other platforms as soon as Hashmart will deploy its tariff plans for validators and a staking calculator. You will be able to receive full-fledged passive income from the new ecosystem without risks or additional costs. Follow the news on our blog to be the first to know about the start of staking!